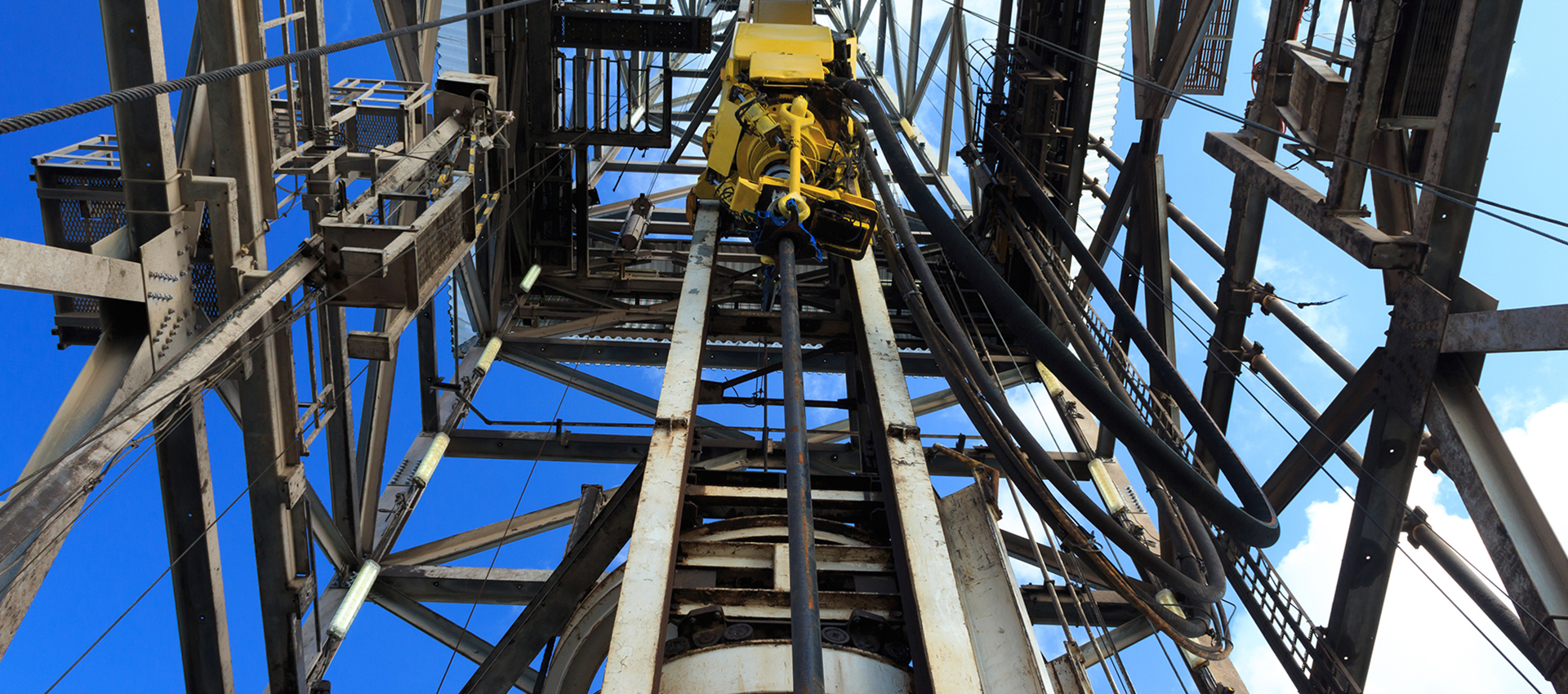
Geological Survey Calibration Blocks
Magnesium is a popular material for oil and drilling calibration blocks due to its lightness, strength, and stability.

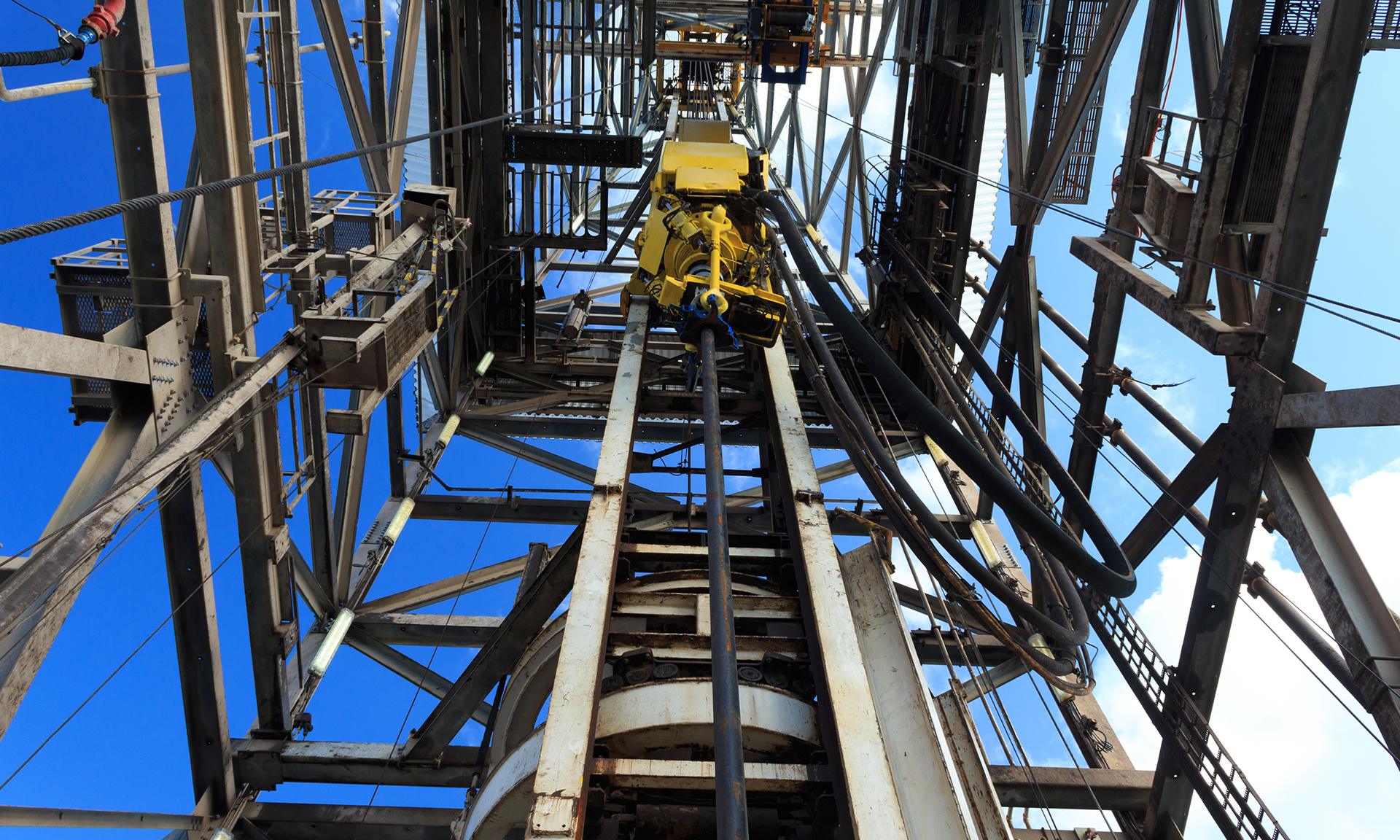
Lightness
Magnesium is one of the lightest metals available, making it ideal for oil and drilling calibration blocks, which need to be lightweight and portable. This is important for reducing the risk of injuries and making it easier to transport the calibration blocks to the drilling site.
Strength
Magnesium alloys are very strong, even at high temperatures and pressures. This makes them ideal for oil and drilling calibration blocks, which need to withstand the harsh conditions of the drilling environment.
Stability
Magnesium alloys are dimensionally stable, meaning that they do not shrink or swell significantly with changes in temperature or humidity. This is important for oil and drilling calibration blocks, which need to maintain their accuracy over a wide range of environmental conditions.

Other benefits
In addition to its lightness, strength, and stability, magnesium also offers a number of other benefits for oil and drilling calibration blocks, including:
- Corrosion resistance: Magnesium alloys are highly resistant to corrosion, which is important for calibration blocks that may be exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
- Machinability: Magnesium alloys are alloys are free-machining, which makes it possible to machine complex calibration block designs in little time.
- Cost-effectiveness: Magnesium is a relatively inexpensive metal, which makes it a cost-effective choice for oil and drilling calibration blocks.

Applications
Magnesium oil and drilling calibration blocks are used to calibrate a variety of instruments used in the oil and drilling industry, including:
- Mud loggers: Mud loggers use magnesium calibration blocks to calibrate their instruments, which are used to measure the properties of drilling mud.
- Wireline loggers: Wireline loggers use magnesium calibration blocks to calibrate their instruments, which are used to measure the properties of the geological formation around.
- Cement loggers: Cement loggers use magnesium calibration blocks to calibrate their instruments, which are used to measure the properties of the cement that is used to line the wellbore.