Medical Equipment
Magnesium use in Portable X-ray Devices, Knee Braces, and Other Medical Products
Magnesium is a versatile and valuable material for a variety of medical products, including portable X-ray devices, knee braces, and other medical devices.
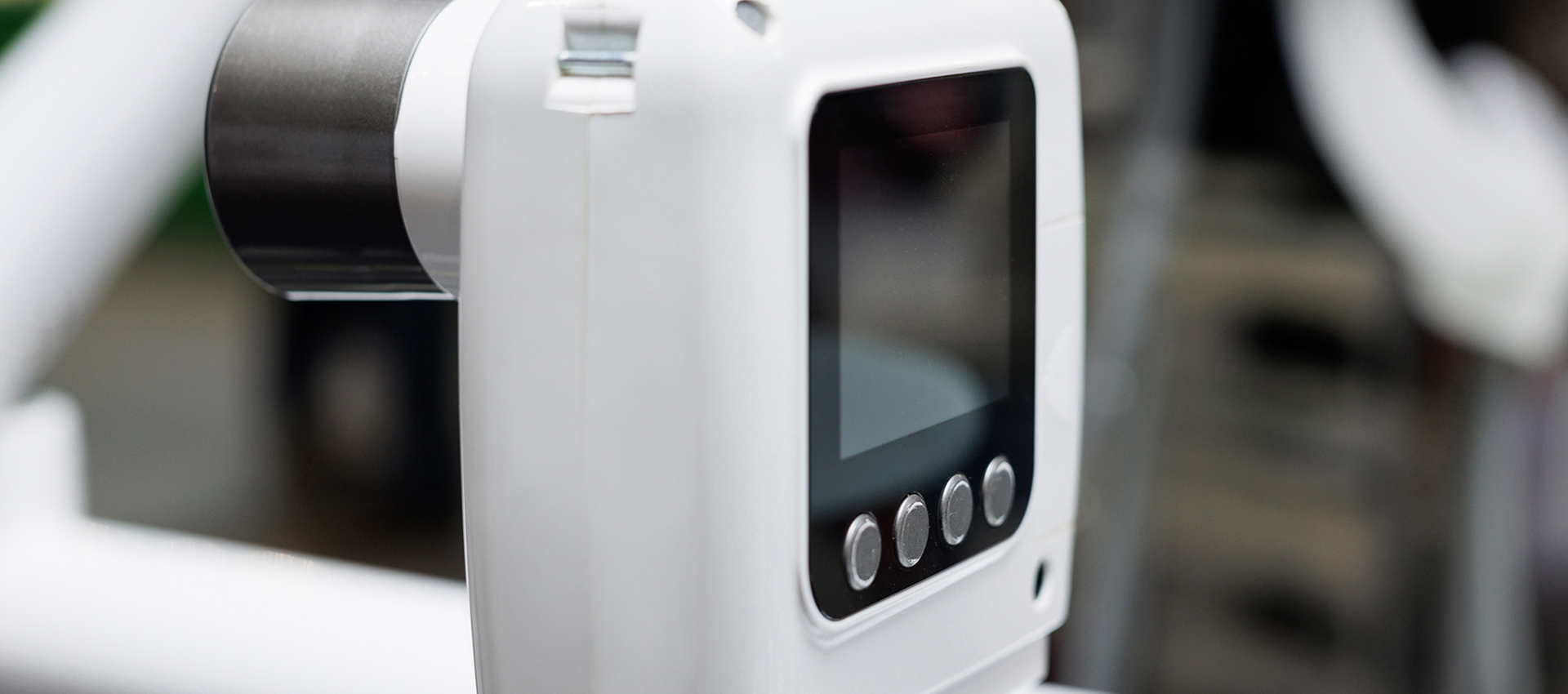


Portable X-ray devices
Magnesium is used in the construction of the housings for portable X-ray devices. Its lightweight and durability make it ideal for this application, as it helps to reduce the weight of the device and improve its portability without concessions on robustness. Magnesium is also resistant to corrosion, which is important for medical devices that may be exposed to harsh environmental. Magnesium is also non-toxic, even in the body.
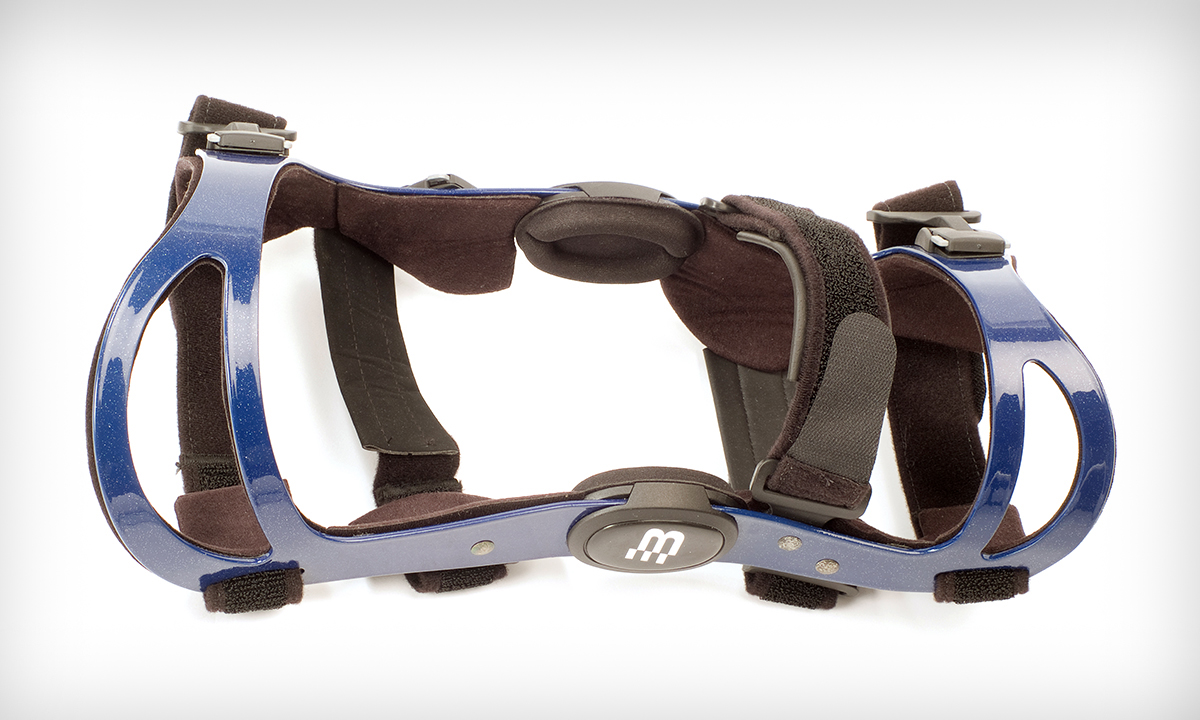

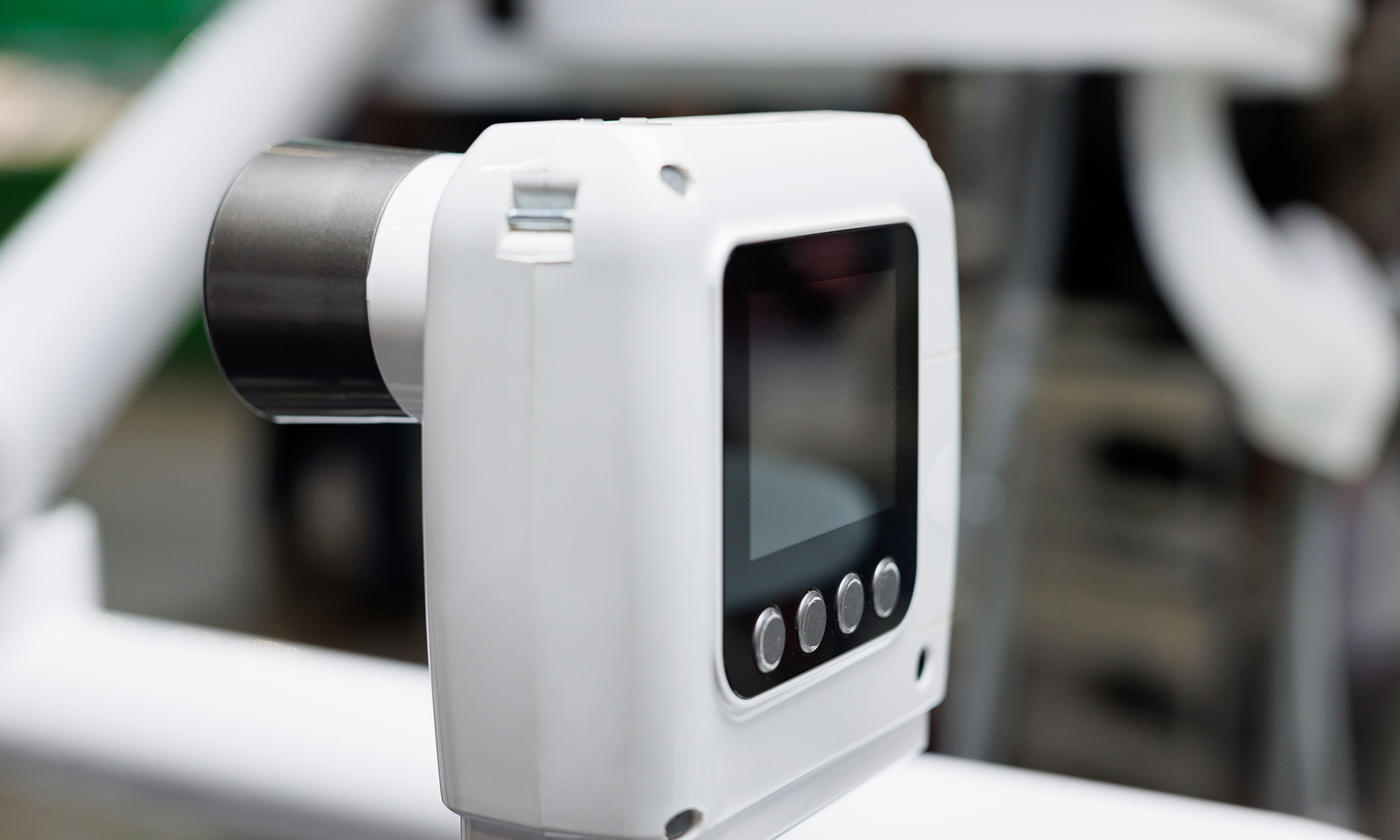
Knee braces
Magnesium is used in the construction of knee braces. Its lightweight and strength make it ideal for this application, as it provides support and protection for the knee without adding significant weight. Magnesium is also resistant to corrosion, which is important for medical devices that may be exposed to sweat and other bodily fluids.
Benefits of using magnesium for medical products
There are a number of benefits to using magnesium for medical products, including:
Lightweight
Magnesium is one of the lightest metals available, which makes it ideal for medical products where weight is a critical factor, such as portable X-ray devices and knee braces.
Strong
Magnesium is one of the lightest metals available, which makes it ideal for medical products where weight is a critical factor, such as portable X-ray devices and knee braces.
Cost-effective
Magnesium is a relatively inexpensive metal, especially compared to other typical implant materials (like titanium), which makes, which makes it a cost-effective choice for medical products.
Corrosion resistant
Magnesium alloys are highly resistant to corrosion, which is important for medical devices that may be exposed to harsh environments, such as the inside of the body or the operating room.
Biocompatible
Magnesium is a biocompatible metal. It is both non-toxic and not rejected by the body. It has a similar elasticity to bone, limiting the bone wear seen when harder materials for implants like titanium are used. It is also gradually biodegradable, allowing for regrowth of the damaged area with the support of the magnesium scaffold without the need for secondary surgical removal to collect the implanted hardware.